Skeletal Muscles: Structure, Type and Working
Skeletal Muscles: Structure, Type and Working: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as sarcomere, agonistic muscles and synergists muscles.
Important Questions on Skeletal Muscles: Structure, Type and Working
Do Synergist muscle assist Prime movers ?
Why Synergist muscle also known as Neutralizer ?
What is the example of Synergist muscle ?
What is Synergist muscle ?
What is the difference between Agonistic and Antagonistic muscles ?
What are example of Antagonistic muscle ?
What are Antagonistic muscle ?
What is Agonistic muscle ?
Fibrous membrane in the middle of a sarcomere is
Fibrous membrane in the middle of sarcomere is
When a skeletal muscle shortens during contraction, which of these statements is false?
Anisotropic bands are made up of
Sarcomere is distance between
The functional unit of contractile system of a striated muscles is
The flexor and extensor muscle of the arm are antagonistic muscles.
Mention structural and functional unit of muscle.
The following diagram represents a sarcomere.
Based on the diagram, use the terms - A-Band, H-Zone, I-Band and Z-Line to label the structures represented by A, B, C and D.
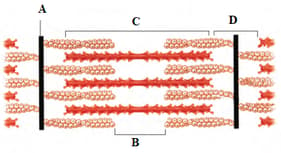
Statements:
A. A-bands of the muscle are dark and contain myosin.
B. I-bands are the light bands and contain actin.
C. During muscle contraction the A-band contracts.
D. The part between the two Z-lines is called as sarcomere.
E. The central part of thin filament, not overlapped by thick filament is called H-zone.
With respect to the above statements select the correct option.
Which of the following is a component of actin filaments of a sarcomere?
